- TEL:
- +81-3-5462-4831
- FAX:
- +81-3-5462-4835
※9:00-17:40 Mon.-Fri. (JST)


Susumu Ohya, Hiroaki Kito, Junko Kajikuri , Yohei Yamaguchi and Miki Matsui
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6019. | https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25116019
Copyright © Authors 2024
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY).
The tumor suppressor FBXW7 is known to reduce cancer stem cell properties by promoting the proteolysis of pluripotent stem cell markers. Meanwhile, KCa1.1 (calcium-activated potassium channel) has been reported to be involved in cancer cell proliferation and cancer stem cell properties, with its inhibition demonstrating tumor suppressor effects. The authors have previously demonstrated that FBXW7 is an essential regulator of KCa1.1 protein degradation in several cancers. However, the molecular mechanisms and detailed intracellular signaling pathways by which KCa1.1 inhibition affects cancer stem cell properties via FBXW7 transcriptional regulation remain unclear.
|
This study aimed to investigate the KCa1.1 inhibition-mediated regulation of FBXW7 expression and its associated signaling cascades in KCa1.1-expressing cancer cells. The authors found that inhibition of the Ca²⁺-activated K channel KCa1.1 in 3D model of human prostate cancer (LNCaP cells) promotes FBXW7 transcriptional activity through the Akt-Nrf2 signal pathway. |
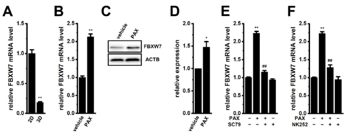
Effects of the treatment with PAX on FBXW7 expression and effects of Akt and Nrf2 activation on the KCa1.1 inhibition-induced up-regulation of FBXW7 in the 3D spheroid model of LNCaP cell 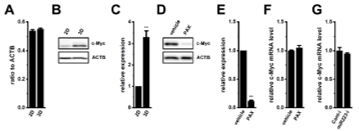
Effects of the treatment with PAX on c-Myc expression in the LNCaP spheroid model. |
Plate: PrimeSurface™ 96U plate
Cell: LNCaP cells; Cell density: 1x104 cells/well; Medium: RPMI 1640 medium (10% FBS)
Methods and Results:
3D spheroid culture more closely mimics the in vivo environment than 2D culture, so the spheroid model was used. Gene and protein expression were performed using real-time PCR and Western blot analysis. Treatment with PAX, a KCa1.1 inhibitor, for 12 hours significantly increased FBXW7 expression in the spheroids and decreased the protein expression of c-Myc, a pluripotency marker. Furthermore, Ark and the Nrf2 signal activators SC79 and NK252 also used to confirm FBXW7 protein expression. These results suggested that inhibition of KCa1.1 via the Akt-Nrf2 signaling pathway promotes FBXW7 transcriptional activity, accelerates protein degradation, and suppresses cancer stem cell stemness.
(For details, please refer to the paper)
| Cat # | Product name | Well | Color | Bottom design | Well Vol | Package |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS-9096UZ | PrimeSurface™ 96U | 96 | Transparent | U bottom | 300 μL | Individual packaging 20 plates per case |
Remark