- TEL:
- +81-3-5462-4831
- FAX:
- +81-3-5462-4835
※9:00-17:40 Mon.-Fri. (JST)


Ana Vujic, Marija Klasic, Gordan Lauc, Ozren Polašek, Vlatka Zoldoš and Aleksandar Vojta
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(18), 9988; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25189988
Copyright: © 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland.
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY).
IgG glycosylation affects its function, with Fc glycosylation at Asn-297 modulating structure, receptor interactions, and inflammation. Fab glycosylation, introduced by somatic hypermutation, impacts antigen-binding and half-life. Glycosylation varies with disease, aging, and individual genetic and environmental factors.
|
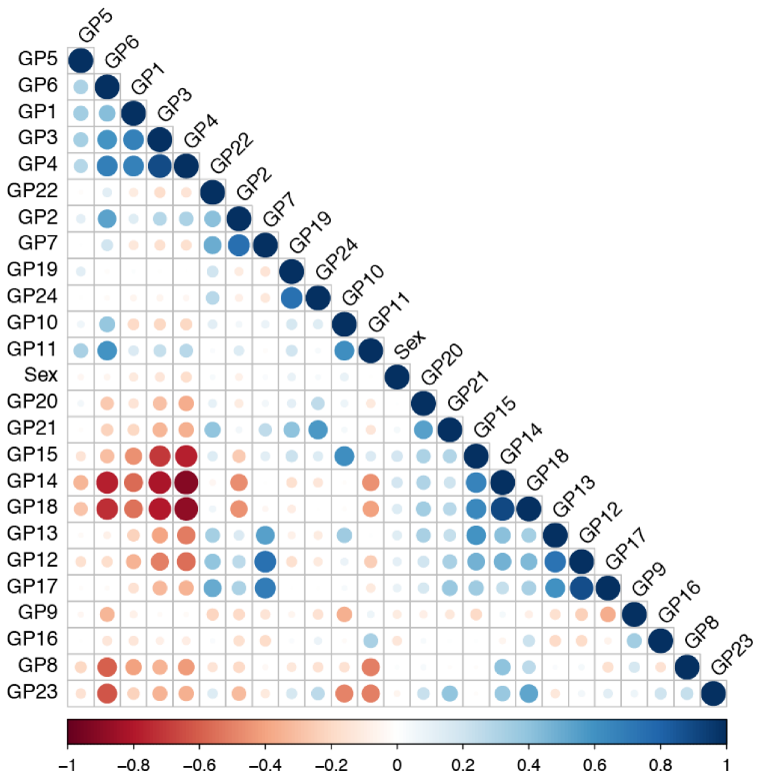
This study focuses on the glycosylation of IgG (immunoglobulin G) and its close association with physiological states and diseases. The authors aimed to predict biochemical and physiological parameters using deep learning models trained on IgG glycome composition data. Glycosylation of IgG is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors, making the glycome a potential biomarker for specific health conditions and diseases. Using data collected from study participants, including IgG glycome compositions and corresponding biochemical and physiological parameters (e.g., age, sex, BMI, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, etc.), the authors developed a deep learning model capable of accurately predicting these parameters. |
|
Furthermore, specific glycan features within the IgG glycome were identified as indicative of certain physiological states or diseases. These findings highlight the utility of IgG glycome as a promising biomarker for personalized medicine and disease prediction.
This research introduces a novel approach by integrating artificial intelligence (specifically deep learning) with biomarker studies, underscoring the importance of data-driven methodologies in the biomedical field. The study’s outcomes suggest that this approach could be extended to other diseases and parameters, paving the way for broader applications in personalized healthcare.