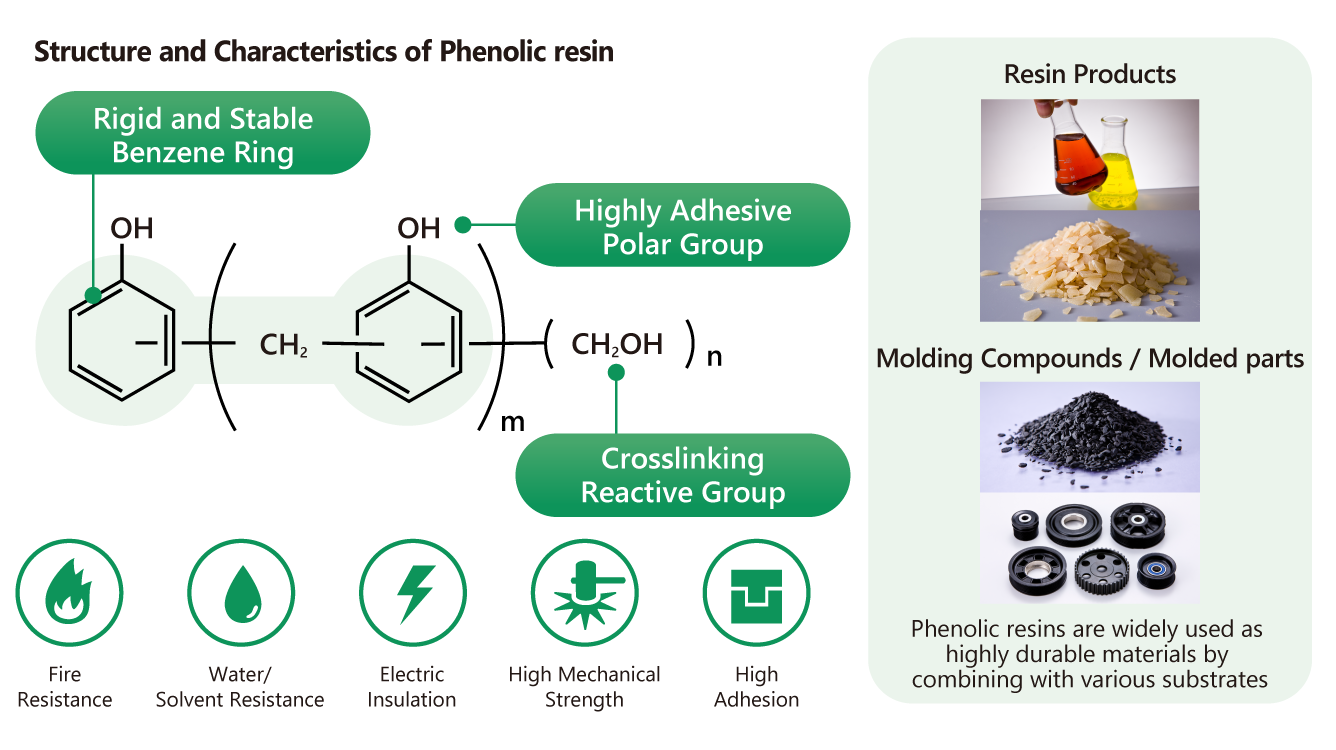
Biomass utilization for high-performance thermosetting resins
SBHPP (High Performance Plastics Business of Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd.) provides
high-performance thermosetting resin materials such as phenolic resins.
We have been working on resource circulation and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions while aiming for new
functions and higher durability. As part of these efforts, we are promoting the use of biomass.
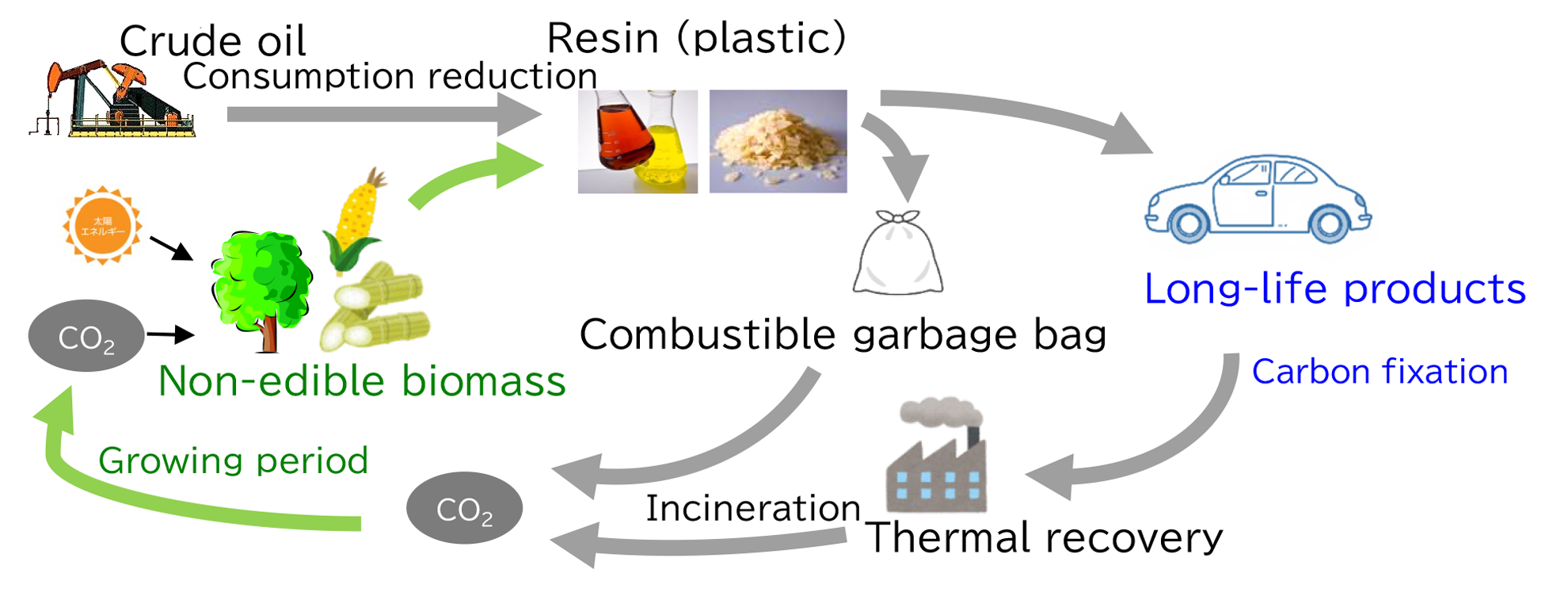
Biomass grows by absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. Substituting biomass-derived resources for
fossil-derived resources used in plastics (resins) can substantially reduce CO2 emissions from
incineration.
Biomass can also be circulated as carbon.
On the other hand, the use of biomass for plastics requires consideration of factors such as interference
with the 3Rs (Reduce,
Reuse, Recycle), competition with food, and various environmental impacts (Greenhouse gases and water) over
the life cycle.
*It has been pointed out that the use of biomass for “unnecessary” single-use plastics interferes with the 3Rs. It has also been pointed out that it cannot be circulated if growing period of biomass is much longer than plastic product life.
In Japan, “Utilizing biomass in cases where the 3Rs are difficult, such as when plastic is essential for function and is inevitably incinerated due to the nature of the product (e.g., combustible garbage bags)” has been advocated.
*It means to utilize renewable (Reduction in use and resource conservation) after
thoroughly implementing the 3 Rs of Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle.
Refference: 2019 Plastic Resources Strategy “Principle of 3R+ Renewable”
If the product has a long life, the carbon captured by biomass can be fixed for a long time.
As in these examples, it is necessary to think about plastic products suitable for biomass.
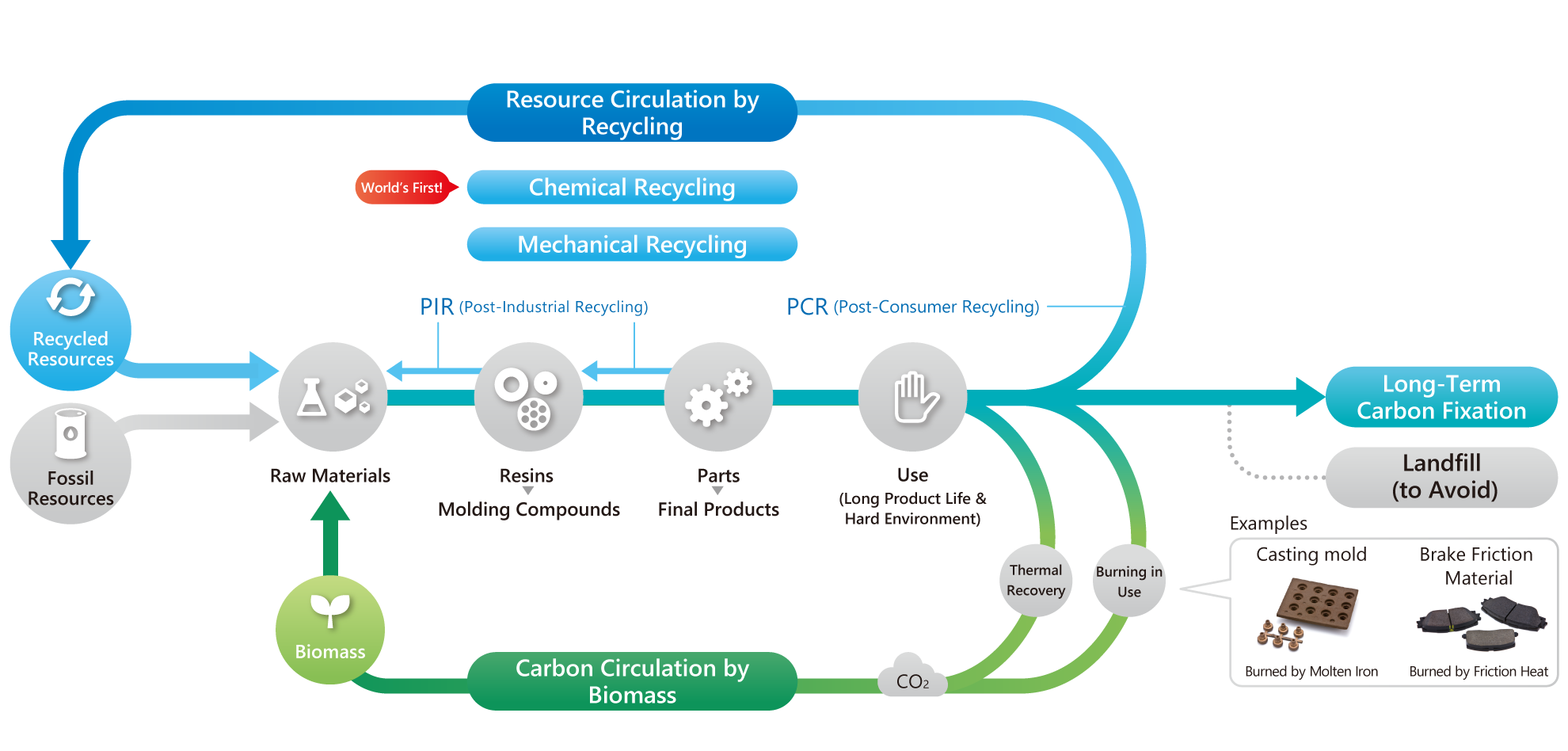
Example of appropriate biomass utilization for plastics
Utilization of biomass in phenolic resins
Here are some examples of phenolic resin products that are highly resistant to heat and light.
Ex.1: Heat-resistant products such as molds and friction materials are exposed to extremely high
temperatures during use, causing them to decompose or burn.
Ex.2: High-strength products such as automobile parts can be used without deterioration for more than 10
years until being scrapped.
As described above, we aim to apply biomass to products that are functionally essential and are difficult
to recycle or have a long life.
Life Cycle of Phenolic Resin Products
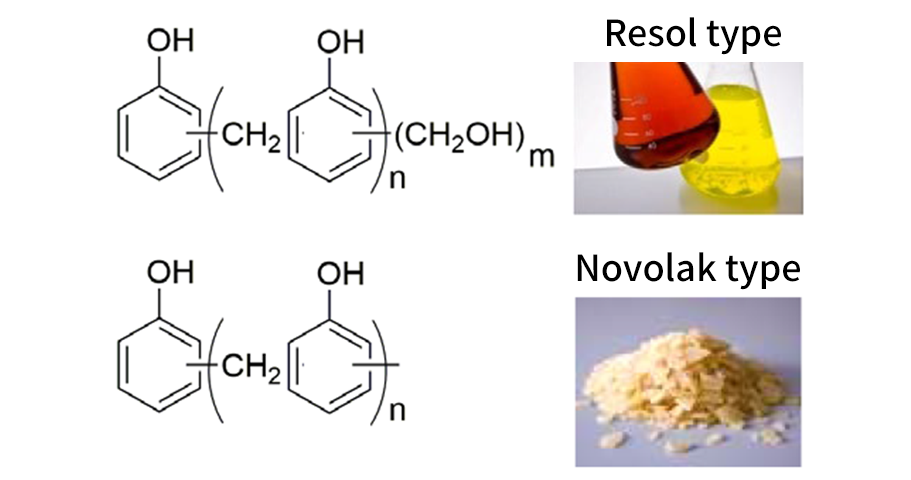
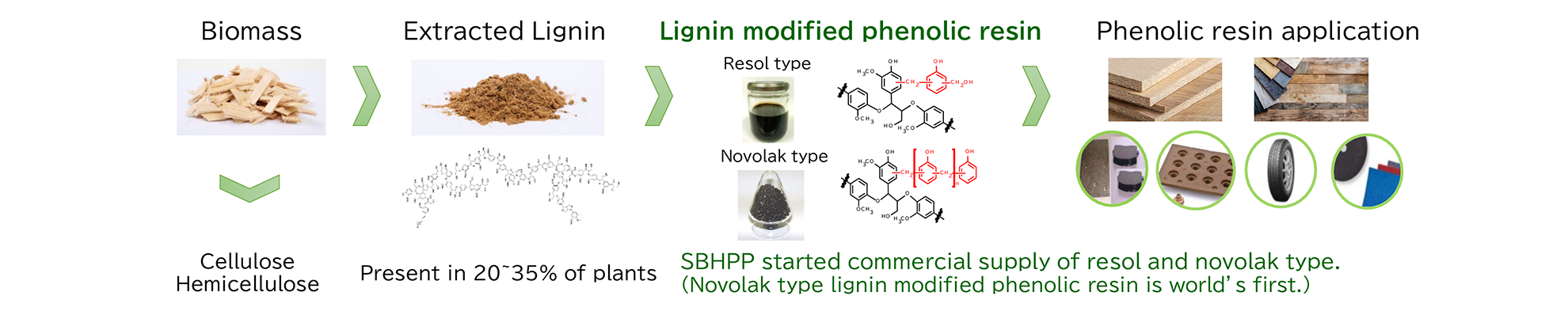
Biomass phenolic resins
As a leading phenolic resin supplier, SBHPP has been working on biomass utilization for
phenolic resins.
SBHPP have been providing biomass phenolic resins with various functions over many years. They are used for
applications that take advantage of flexibility, hydrophobicity, and adhesiveness derived from biomass.
In recent years, SBHPP have developed lignin-modified phenolic resins with excellent durability and have
been applying them to conventional applications. SBHPP are also developing new applications that take
advantage of the unique functions of lignin.
Conventional Phenolic Resin
(Rigidity, strength, and heat resistance)
Conventional
Biomass Modified Phenolic Resin
(Flexibility, hydrophobicity, adhesion, etc.)
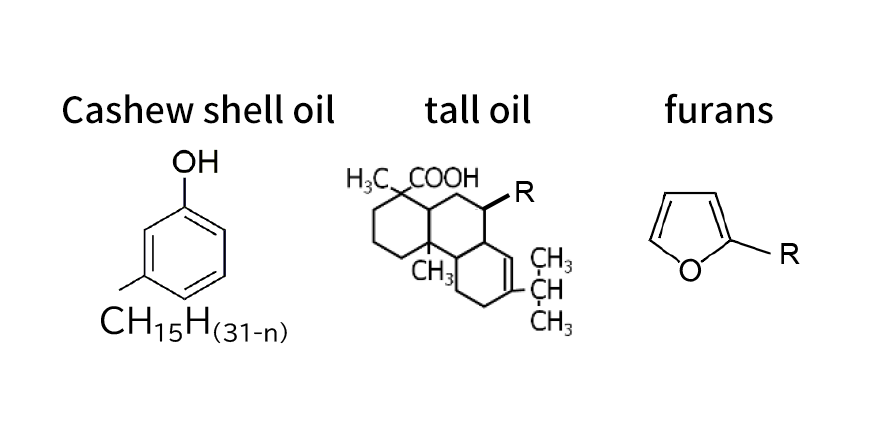
Lignin-modified phenolic resins
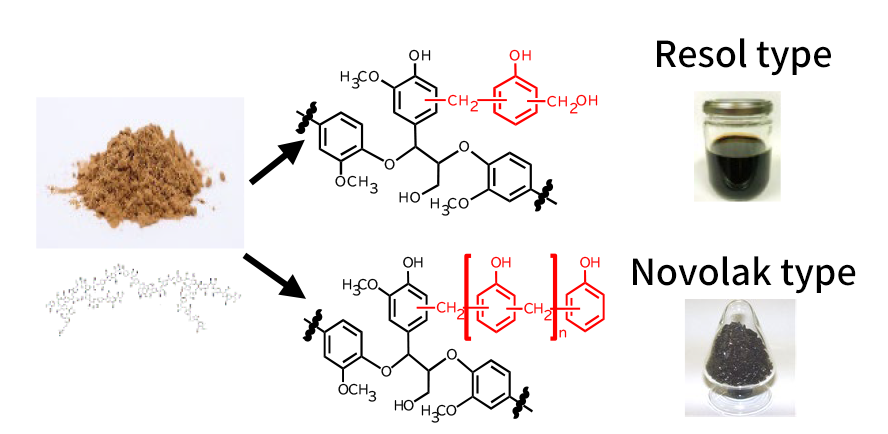
conventional resin
Functions unique to lignin
“Old and New” Lignin-modified phenolic resins
Lignin is one of the three main components of plants and is a non-edible biomass with a phenolic
skeleton.
By appropriately incorporating a variety of lignins into phenolic resins, SBHPP is developing
and implementing biomass phenolic resins with higher functionality than conventional products.
Highly durable biomass network polymer
SBHPP is developing a biomass network polymer that can replace or even surpass phenolic resins.
The proportion of non-edible biomass of the biomass network polymers is close to 100%.
*A polymer (resin or rubber) crosslinked by thermosetting is called a network
polymer. Thermosetting resins are also included in network polymer.
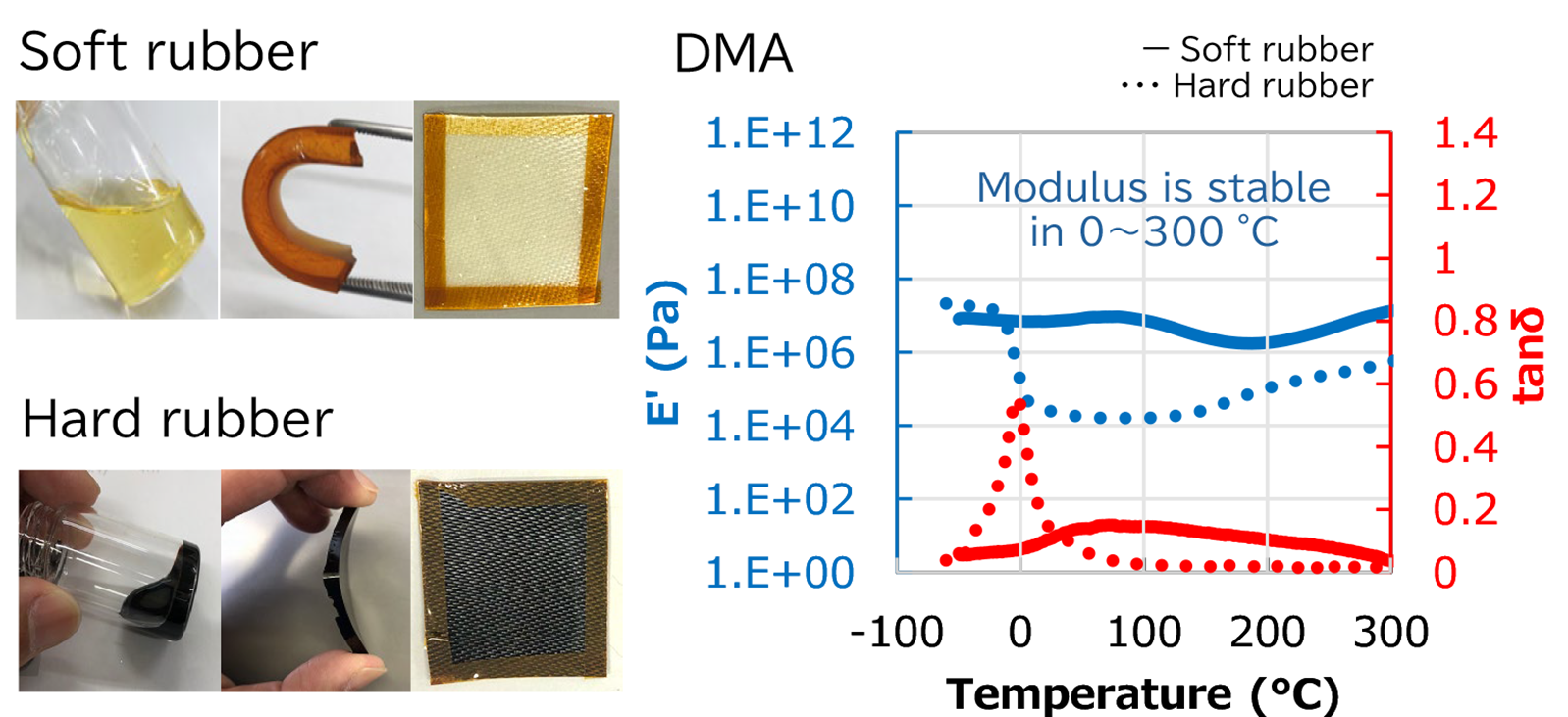
(Thermal decomposition is also suppressed).
Highly durable biomass network polymer to meet diversifying needs.
Topics More
- 2026/01/30ProductsDevelopment of Biomass PFA Resin-Based Prepreg with Superior Flame Retardancy for Aircraft Interior Materials
- 2026/01/15ProductsAdoption of Heat-Dissipating Insulating Sheet in Resin-Insulated Substrate Integrated Power Module
- 2026/01/13ProductsSustainability Topics: Launch of the Website Towards the Sustainability of Phenolic Resins
- 2026/01/13ProductsInitiatives for Mechanical Recycling of Phenolic Resin Products
- 2025/11/13ProductsLaunch of Mass Production of the Main Deck Cargo Liner for Airbus' New A350F Freighter Aircraft

 Inquiry
Inquiry