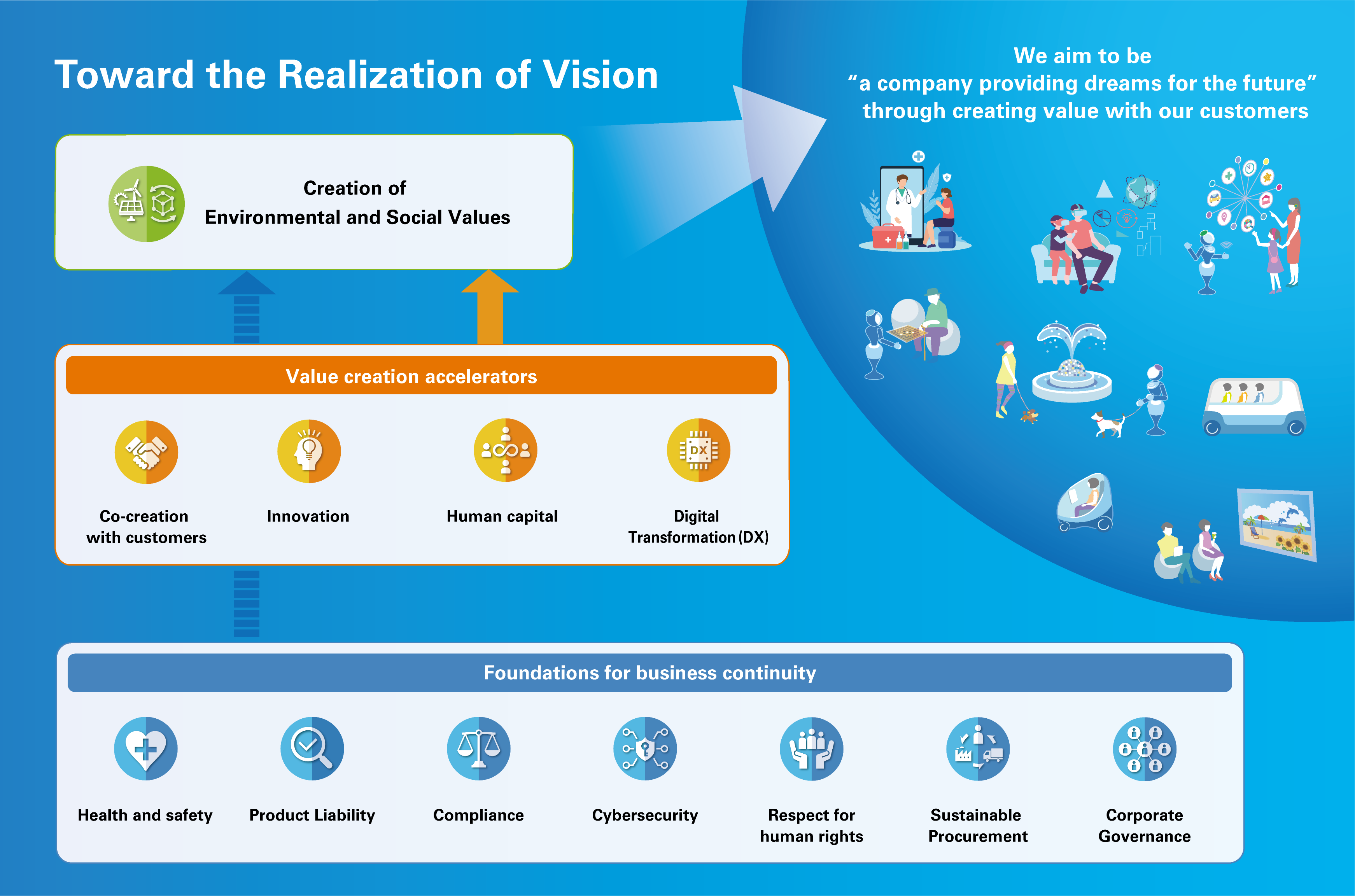
Redefining material issues with backcasting, pursuing the creation of environmental and social values
Aiming to realize our vision for 2030 of being a “company providing dreams for the future” through
creating value with our customers, we identified 12 material issues in FY2024.
Creation of environmental and social values is about creating value that will directly contribute to
achieving our vision for 2030. Co-creation with customers, innovation, human capital, and digital
transformation will propel our efforts to create environmental and social values, so we have positioned
these issues as value creation accelerators in view of their anticipated effects. Finally, the seven
foundations for business continuity are vital issues that form the basis of these efforts.
KPIs for Material Issues
We have set KPIs to clarify our specific efforts to address each of the 12 material issues. The Sustainability Promotion Committee regularly checks progress as we work on these KPIs.
| Material Issues | KPIs | FY2030 Targets | FY2024 Results | |||
| Creation of environmental and social values | ❶ SDG-contributing product revenue ratio | 70% or higher | 66.4% | |||
| ❷ GHG emissions reduction*1 compared to FY2021 | 48% or higher | 45% | ||||
| Value creation accelerators | Co-creation with customers | ❶ Number of themes co-created with customers as a result of One Sumibe Activities (per year) | 10 co-creation themes | 11 co-creation themes | ||
| ❷ Number of cross-department based in-house exhibitions held (per year) | 8 | 11 | ||||
| Innovation | ❶ Number of projects implemented | 5 or more | 6 | |||
| ❷ Contribution to business profit | ¥10.0 billion | ― | ||||
| Human capital | ❶ Promotion of diversity | (1) Promote the advancement of women | • Ratio of female management staff (non-consolidated) | 10% | 4.25% | |
| • Ratio of new fathers taking childcare leave (non-consolidated) | 90% | 84% | ||||
| (2) Ratio of mid-career hires (non-consolidated)*2 | 50% | 43% | ||||
| ❷ Enhancement of autonomy Number of employees participating in 360° assessment-based education programs |
70 | 52 | ||||
| ❸ Enhancement of organizational strength Number of employees participating in management education programs |
70 | 58 | ||||
| Digital transformation | ❶ Core system integration | Core system data integration (global) | Conceptualization completed | |||
| ❷ Human productivity*3 | (1) Production departments*4 | 2.0 | 1.1 | |||
| (2) Management departments*5 | 2.0 | 1.1 | ||||
| ❸ Number of trained data scientists: | (1) Number of employees with data science-related certifications | 150 | 54 | |||
| (2) Number of employees that possess data science-related skills | 450 | 145 | ||||
| Foundations for business continuity | Health and safety | ❶ Serious occupational accidents (per year) | 0 | 2 | ||
| ❷ Accidents caused by fire and/or explosion, resulting in operational stoppage (per year) | 0 | 0 | ||||
| ❸ Number of data leaks (per year) | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Product liability | ❶ Critical quality complaints (per year) | 0 | 0 | |||
| Compliance | ❶ Compliance training participation rate | 100% | 100% | |||
| ❷ Number of serious compliance violations (per year) | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Cybersecurity | ❶ Major cybersecurity incidents (per year) | 0 | 0 | |||
| ❷ Cybersecurity training participation rate | 100% | 100% | ||||
| ❸ Cybersecurity incident response training (times held per year) (non-consolidated) | twice | twice | ||||
| Respect for human rights | ❶ Human rights due diligence | Conduct human rights due diligence | Priority issue identification completed | |||
| Sustainable procurement | ❶ Sustainable procurement rate*6 | 100% | ≧85% | |||
| ❷ Usage rate of smelters conforming to RMAP related to 3TG*7 | 100% | 100% | ||||
| Corporate governance | ❶ Continuous improvement of the effectiveness of the Board of Directors from the viewpoint of board composition and operation | Evaluate the effectiveness of the Board of Directors and address priority issues | Effectiveness evaluation of the Board of Directors and implementation of measures to address priority issues completed | |||
- *1 Scope1 and Scope 2 emissions
- *2 Career track recruits
- *3 2023 is set as 1.
- *4 Calculated based on marginal profit/direct man-hour for major products.
- *5 Calculated for management departments and the Information Systems & Data Processing Department using the formula target time/ (target time - reduction time).
- *6 The percentage of major suppliers that meet the specified criteria through which the Company makes 90% of purchases by segment based on self-assessment sheets from the JEITA Responsible Business Conduct Guidelines.
- *7 3TG: Tin, Tantalum, Tungsten and Gold, Responsible Minerals Assurance Process (RMAP).
Material issues determination process
Material issues were selected with the following process, which involved first broadly identifying issues and then narrowing down the list of key issues. Based on the results of this process, material issues were arranged and key issues identified with the approval of management.
STEP 1 Identification of issues
We refer to the following to help identify a broad range of issues
- Information regarding social issues
- UN guidelines and external environmental, social, and governance assessment agency items
- Group policies, department initiative details
- Discussions during the Medium-term Business Plan formulation process
- Dialogue with stakeholders
STEP 2 Selection and arrangement of material issues
Highly important issues are selected according to the following two factors
- “Importance to Society”
- “Importance to the Group”
They are arranged in terms of the following in light of expected benefitss
- “Value creation”
- “Value creation accelerators”
- “Foundations for business continuity”
STEP 3 Management deliberation and approval
Determine material issues on approval of the Board of Directors
The Sustainability Promotion Committee confirms the comprehensiveness and appropriateness of the material issues identified, then obtains the approval of the Board of Directors.
Relationship between Material Issues and ESG
| Topics | E | S | G | |
| Creation of Environmental and Social Values | ● | ● | ● | |
| Co-creation with Customers | ● | |||
| Innovation | ● | |||
| Human Capital (Human Resource Participation) Management | ● | |||
| Digital Transformation | ● | |||
| Sustainable procurement | ● | |||
| Occupational health and safety | ● | |||
| Respect for human rights | ● | |||
| Cybersecurity | ● | |||
| Product Liability | ● | |||
| Compliance | ● | |||
| Corporate Governance | ● |