- TEL:
- +81-3-5462-4831
- FAX:
- +81-3-5462-4835
※9:00-17:40 Mon.-Fri. (JST)


Dereje G. Feleke, Bryan M. Montalban, Solomon T. Gizaw and Hiroshi Hinou
International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26.11 (2025): 4968. | https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/26/11/4968
Copyright: © 2025 by authors.
This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license
Conventional biomarkers such as CA15-3 and CEA lack sensitivity and specificity, underscoring the need for more reliable molecular indicators. This study aimed to identify novel serum biomarkers for the early detection of breast cancer by comprehensively analyzing sulfated N-glycans.
This study aimed to identify novel serum biomarkers for the early detection of breast cancer by comprehensively analyzing sulfated N-glycans. Conventional biomarkers such as CA15-3 and CEA lack sensitivity and specificity, underscoring the need for more reliable molecular indicators.
To address this challenge, the researchers employed a glycoblotting-based “sulfoglycomics” workflow, which enables efficient capture and enrichment of glycans through hydrazide-functionalized beads (Glycan Purification and Labeling kit BlotGlyco™ from Sumitomo Bakelite). Combined with weak anion exchange separation and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, this method allowed for the selective detection and quantification of low-abundance sulfated glycans that are otherwise difficult to analyze.
Serum samples from 76 Ethiopian breast cancer patients and 20 healthy controls were examined. The study identified 13 sulfated N-glycans, of which seven mono-sulfated species were significantly elevated in breast cancer sera, particularly in early-stage (I–II) cases, achieving diagnostic accuracies (AUC ≥ 0.8). These glycans frequently exhibited Lewis-type and sialylated terminal epitopes, structural features associated with cancer cell adhesion, immune evasion, and metastasis.
The findings highlight the clinical and social significance of glycomic profiling as a non-invasive approach for early cancer detection. By leveraging glycoblotting, this study provides the first comprehensive quantitative analysis of serum sulfated N-glycans, revealing promising biomarker candidates and offering deeper insight into cancer-associated glycosylation changes. The methodology and results not only enhance our understanding of breast cancer biology but also lay a foundation for applying glycan-based diagnostics across diverse diseases.
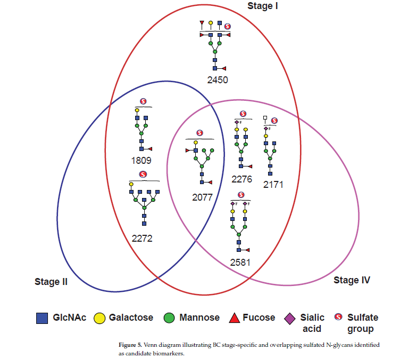
The figure illustrates the upregulation patterns of sulfated N-glycans across different breast cancer stages, demonstrating that specific glycans are distinctly elevated in early-stage breast cancer.
Glycan Purification and Labeling Kit: BlotGlyco™
| Cat No. | Product | Contents | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer beads | aoWR Reaction tube | Cleanup column | ||
| BS-45414 | BlotGlyco™ 10B | 10 | 10 | 10 |
Remark